GAIA is a space observatory of the ESA which is going to list approximately 1 billion (109) of components of the universe. Each will be approximately observed 70 times during 5 years of the telescope’s life. GAIA was successfully launched December 19th, 2013 and will reach its point of observation approximately 3 week later.
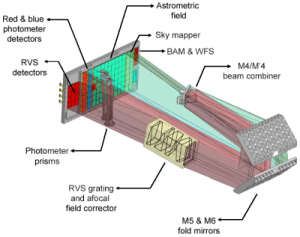
Gaia is composed by 3 instruments:
– Astro: Instrument which is going to determine the position of every star of the galaxy and by its follow-up over 5 years to evaluate their distance and speed.
– The radial velocimeter to measure more exactly the speed of stars.
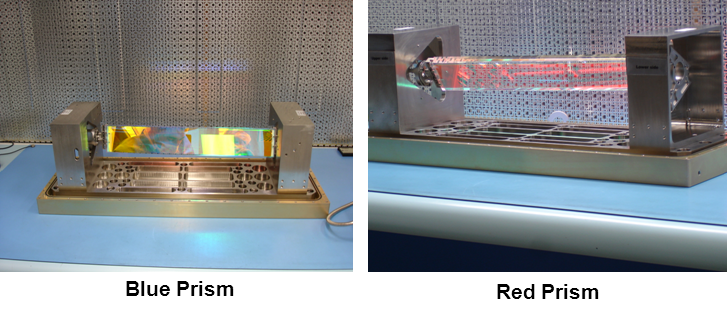
– The photometer which measures the star’s luminosity. It has 2 channels blue and red, which allow determining star’s properties as their T°, mass, age and main composition. The spectral bandwidth of the stars’s light is obtained through 2 prisms manufactured by Thales SESO. The blue prism for 330-680 nm spectral bandwidth and red prism 640-1050 nm. Each prism has a useful length of more than 400 mm and is characterized by its very high quality of optical surface (flatness, roughness).
GAIA is a space observatory of the ESA which is going to list approximately 1 billion (109) of components of the universe. Each will be approximately observed 70 times during 5 years of the telescope’s life. GAIA was successfully launched December 19th, 2013 and will reach its point of observation approximately 3 week later.
Gaia is composed by 3 instruments:
– Astro: Instrument which is going to determine the position of every star of the galaxy and by its follow-up over 5 years to evaluate their distance and speed.
– The radial velocimeter to measure more exactly the speed of stars.
– The photometer which measures the star’s luminosity. It has 2 channels blue and red, which allow determining star’s properties as their T°, mass, age and main composition. The spectral bandwidth of the stars’s light is obtained through 2 prisms manufactured by Thales SESO. The blue prism for 330-680 nm spectral bandwidth and red prism 640-1050 nm. Each prism has a useful length of more than 400 mm and is characterized by its very high quality of optical surface (flatness, roughness).