SARAL – Laser Retro-reflector Array

French/Indian
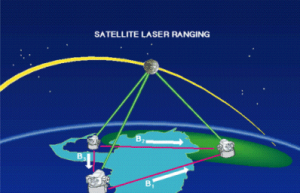
The LRA is a passive instrument on-board a satellite composed of 9 corner cubes reflecting a laser beam back to earth to determine its position. It was part of the SARAL satellite payload and launched on XXXXXX.
Altitude measurement precision of a few millimeters
Corner cubes reflectors have the property to send back to signal where it comes from. On the satellite this property is used to calculate its position from the measured travelling time of a laser from the earth to the satellite, back to earth. A precise measurement of the satellite position yields a precise measurement of the altitudes on earth.

Extra wide field of view
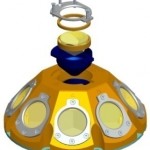 This Laser Retro-reflector Array is composed of 9 corner cubes to provide a field of view of 150° over the full 360° azimuth angle.
This Laser Retro-reflector Array is composed of 9 corner cubes to provide a field of view of 150° over the full 360° azimuth angle.
Thales SESO engineers to ensure excellent performances
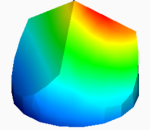 Because of the launch and flight conditions the assembly method had to be robust, stable and precise, as well as compatible with space vacuum and radiations. Thermo-optical and optical analyses were done for each corner cube to simulate the optical gradients.
Because of the launch and flight conditions the assembly method had to be robust, stable and precise, as well as compatible with space vacuum and radiations. Thermo-optical and optical analyses were done for each corner cube to simulate the optical gradients.